Android学习笔记-保存文件(Saving Files)
Android设备有两种文件存储区域:
内部存储和外部存储 ("internal" and "external" storage)。
这名字来自早期Android,那时大多数Android设备提供两种存储方式:内置的非易失的内存(内部存储)和可移动的存储例如micro SD卡(外部存储)。
一些设备将永久内存分为内部和外部两部分,因此即使没有外部存储,依旧有两种存储空间。不管有没有外部存储,API的方法都是一样的。
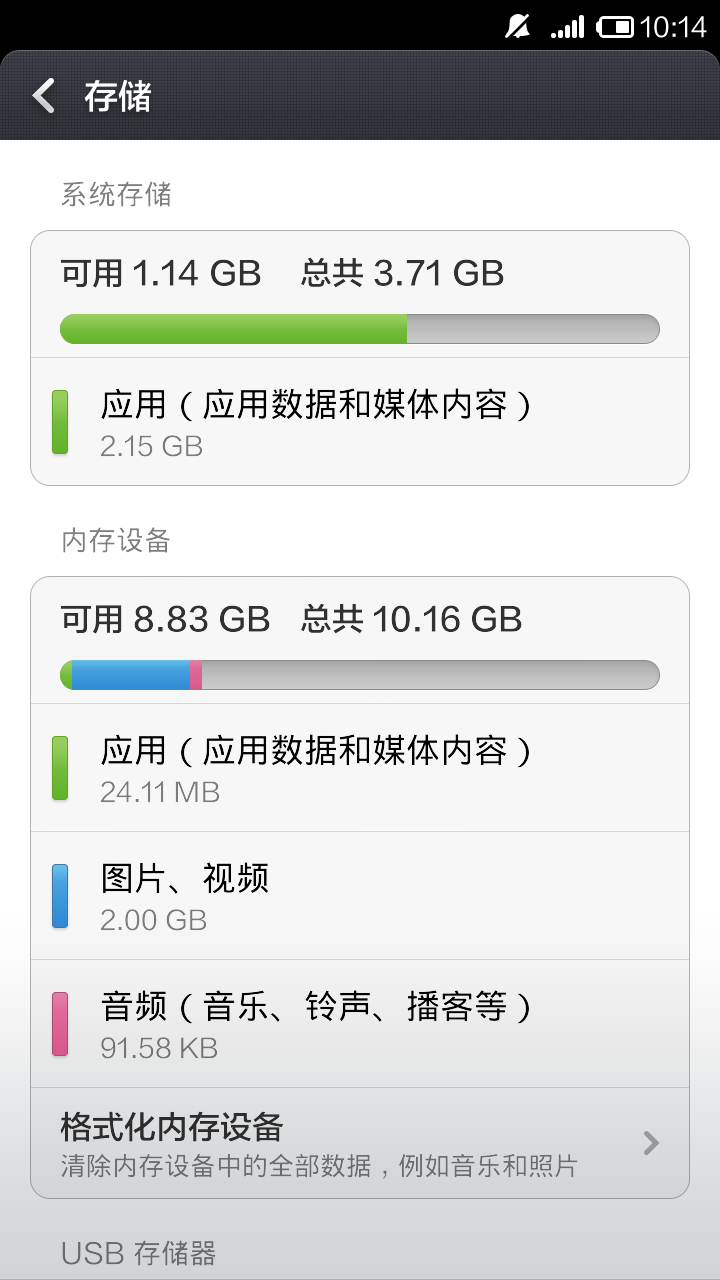
如我的手机小米2S是16G大小的RAM,不支持SD卡的拓展。它将存储分为了内外两部分,3.71G的系统存储(即内部存储),10.16G的内存设备(即外部存储),如下图所示:
内部存储:
始终都是可用的
保存的文件只能被你的app以默认的方式访问
卸载app,系统从内部存储中删除你app的所有文件
内部存储适用于你不想用户或其他app访问你的文件
外部存储:
不总是可用的(用户可能将外部存储以USB方式连接, 一些情况下会从设备中移除)
是全局可读的(world-readable),因此一些文件可能不受控制地被读取
卸载app,只删除你存储在getExternalFilesDir()目录下的文件
外部存储适用于不需要存储限制的文件以及你想要与其他app共享的文件或者是允许用户用电脑访问的文件
app默认安装在内部存储中,通过指定android:installLocation 属性值可以让app安装在外部存储中。
获取外部存储权限:
读与写:
<manifest ...>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
...
</manifest>
读:
<manifest ...>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
...
</manifest>
在内部存储保存文件不需要任何权限,你的app在内部存储中总是有读写权限。
在内部存储中保存文件:
获取适当的目录:
getFilesDir() app文件在内部存储中的目录
eg:
File file = new File(context.getFilesDir(), filename);
getCacheDir() app临时缓存文件在内部存储中的目录
调用openFileOutput()获取FileOutputStream写入文件到内部目录
eg:
String filename = "myfile";
String string = "Hello world!";
FileOutputStream outputStream;
try {
outputStream = openFileOutput(filename, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
outputStream.write(string.getBytes());
outputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
调用 createTempFile()缓存一些文件:
public File getTempFile(Context context, String url) {
File file;
try {
String fileName = Uri.parse(url).getLastPathSegment();
file = File.createTempFile(fileName, null, context.getCacheDir());
catch (IOException e) {
// Error while creating file
}
return file;
}
在外部存储中保存文件:
由于外部存储不总是可用的,正如上面所提到的,用户可能移除了SD卡或USB模式连接了电脑。所有在访问之前需要确认外部存储是可用的。
可以调用 getExternalStorageState() 返回外部存储的状态,如果返回的是MEDIA_MOUNTED,则可以读写在外部存储的文件。
//判断外部存储是否可以读写
public boolean isExternalStorageWritable() {
String state = Environment.getExternalStorageState();
if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(state)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}





